Centre International de Neurobiologie Appliquée selon Dr. Klinghardt
International Center for Applied Neurobiology according to Dr. Klinghardt |
The Klinghardt Neurotoxin Elimination Protocol

Detox mechanisms include acetylation, sulfation, glucuronidation, oxidation and others. Often the host is triggered to produce neurotoxins (which are damaging to their own tissues) by the invading microbes through molecular trickery. The liver is most important in the toxion elimination process. Here most elimination products are expelled with the bile into the small intestine and should leave the body via the digestive tract. However, because of the lipophilic/neurotropic nature of the neurotoxins, most are reabsorbed by the abundant nerve endings of the enteric nervous system (ENS) in the intestinal wall. The ENS has more neurons than the spinal chord.
From the moment of mucosal uptake the toxins can potentially take four different paths:
Here is an incomplete list of common neurotoxins in order of importance:
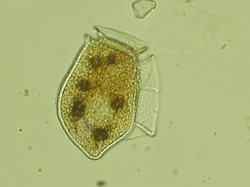
Biotoxins are minute molecules (200-1000 kilodaltons) containing nitrogen and sulfur. They belong to a group of chemical messengers which microorganisms use to control the host's immune system, host behavior and the host's eating habits.
I have found that mercury in its different chemical forms has a synergistic amplifying effect with all other neurotoxins. When mercury is removed, the body starts to more effectively eliminate all other neurotoxins, even if they are not addressed.
The symptoms are: fatigue, depression, insomnia, memory loss and blunting of the senses are common early symptoms (see list of mercury related symptoms on the following pages).
1. History of Exposure: (Did you ever have any amalgam fillings? A tick bite? Etc.)
2. Symptoms: (How is your short term memory? Do you have areas of numbness, strange sensations)
3. Laboratory Testing: (Metals: hair, stool, serum, whole blood, urine analysis, xenobiotics: fatty tissue biopsy, urine. Mold: Immunosciences mold panel)
4. Autonomic Response Testing: (Dr. Dietrich Klinghardt M.D., Ph.D.)
5. BioEnergetic Testing (EAV, kinesiology etc.)
6. Response to Therapeutic Trial
7. Functional Acuity Contrast Test (measure of Retinal Blood Flow)
Why would we want to treat anyone at all? Is it really needed? Can the body not eliminate these toxins naturally on its own?
Here is a short list of independent risk factors which can either cause accumulation of metals in an otherwise healthy body -or slow down, or inhibit the body's own elimination processes.
We will discuss here only those elimination agents, which are natural, safe and have also been shown to be as effective (or more effective) than the few available pharmaceuticals.

This kitchen herb is capable of mobilizing mercury, cadmium, lead and aluminum in both bones and the central nervous system. BioPure cilantro uses a special seed from Brazil that is grown under conditions and in soil that enhances its detox power. It is probably the only effective agent in mobilizing mercury stored in the intracellular space and in the nucleus of the cell (reversing DNA damage of mercury).
Dosage and application of BioPure cilantro tincture: give 10 drops in hot water at bedtime or 30 minutes after taking chlorella. Gradually increase dose to 10 drops 3 times/day for full benefit. During the initial phase of the detox cilantro should be given 5 days on, 2 days off.

Both C.pyreneidosa (better absorption of toxins, but harder to digest) and C.vulgaris (higher CGF content – see below, easier to digest, less metal absorbing capability) are available. We only recommend BioPure chlorella.
Chlorella has multiple published health inducing effects: Antiviral (especially effective against the cytomegaly virus from the herpes family); Toxin binding (mucopolysaccharide membrane) all known toxic metals, environmental toxins such as dioxin and others; Repairs and activates the body's detoxification functions; Dramatically increases intra-cellular reduced glutathione; Super nutrient: 50-60% amino acid content, ideal nutrient for vegetarians; Immune system strengthening.
Dosage: start with 1 gram (=4 tablets) 3-4 times/day. This is the standard maintenance dosage for grown ups for the 6-24 months of active detox. During the more active phase of the detox (every 2-4 weeks for 1 week), whenever cilantro is given, the dose can be increased to 3 grams 3-4 times per day (1 week on, 2-4 weeks back down to the maintenance dosage). Take 30 minutes before the main meals and at bedtime.
Garlic has been shown to protect the white and red blood cells from oxidative damage, caused by metals in the blood stream -on their way out – and also has its own valid detoxification functions. Garlic also contains the most important mineral which protects from mercury toxicity, bio active selenium.
Dosage: 1-3 capsules freeze dried garlic after each meal. Start with 1 capsule after the main meal per day, slowly increase to the higher dosage. Initially the patient may experience die-off reactions (from killing pathogenic fungal or bacterial organisms). Use 5-10 drops bear-garlic on food at least 3 times per day.
The fatty acid complexes EPA and DHA in fish oil make the red and white blood cells more flexible thus improving the microcirculation of the brain, heart and other tissues. All detoxification functions depend on optimal oxygen delivery and blood flow. EPA and DHA protect the brain from viral infections and are needed for the development of intelligence and eye-sight.
Dosage: 1 capsule Omega 3 taken 4 times/day during the active phase of treatment, 1 caps. twice/day for maintenance. Best if taken together with chlorella.
The autonomic nervous system in most toxic patients is dysfunctional. Electric messages in the organism are not received, are misunderstood or misinterpreted. Toxins cannot be shuttled through the extracellular space. Increased intake of natural ocean salt – and avoidance of regular table salt -has been found to be very effective in resolving some of these problems. I recommend "Matrix Electrolyte" to all my patients.
Dosage: 1 tsp in a cup of good water 1-3 times/day Gradually increase the dosage to 1 tbsp 3 times/day
Soy derived phospholipids, magnesium, alpha-lipoic acid and Na-EDTA. This magical mix encourages the "everse cholesterol transport" (taking deposits out of endothelium), has a strong anti-microbial effect and detoxes neurotoxins including mercury in the cell wall and probably inside the cell as well. Long term results are dramatic especially in the treatment of Lyme related heart problems and in treating disturbed microcirculation of the frontal lobe of the brain.

It appears that Lyme spirochetes are highly intelligent and have learned to a large degree to live with us and manipulate our system to their advantage. Our health becomes compromised, but only rarely severely. This adaptation of Bb points towards the fact that Bb or close relatives have been with us for a long time (10s of thousands of years).
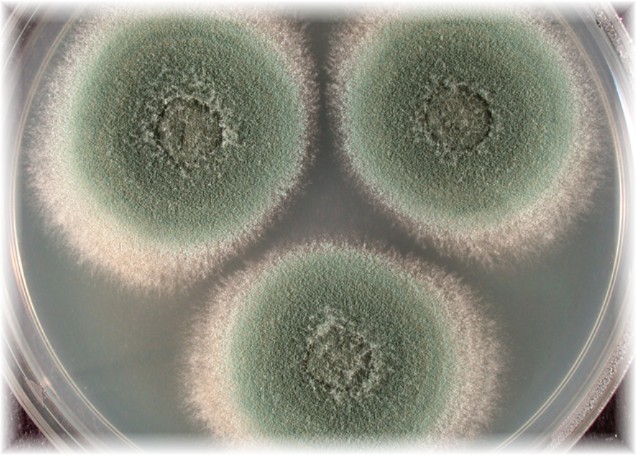
Many fungi produce toxic metabolites called mycotoxins, many of which are neurotoxic. Over 100 species known to cause infection in humans.
Three classifications of infection:
1. systemic (by inhalation): in healthy individuals self limited illness, in immune suppressed individuals may disseminate (generally fatal).
2. opportunistic infection (common in Lyme and as result of heavy metal toxicity): facultative parasites – can use living and dead substrates for nutrition.
3. Dermatophytes (hair, skin and nails). Usually contracted by direct contact through sharing grooming utensils, showers, and towels). Also passed on via soil.
4. Mycotoxins
Most symptoms of heavy metal toxicity, mold exposure, Lyme disease and parasite infestation often look identical. Here is a way to differentiate:
Tip #1: Lyme symptoms worsen during and after successful mercury detoxification (Hg-poisoning was successfully used as a treatment for spirochetes. After eliminating Hg, the microbes recover before the host immune system does). Mold symptoms improve after successful Hg removal (mold uses Hg to protect itself from the host immune system)
Tip#2: Lyme arthritis affects the large joints, mostly knee and hip. Mold arthritis affects the small joints of the spine (facet joints) and of the fingers.
Tip#3: rythms and biorythms: mold symptoms can flare up within minutes after exposure (ie visiting someone who lives in a moldy home). Lyme symptoms undulate with slower biorythms: 9-10 day cycles, 28-day cycles . When symptoms come back, usually slow rise in intensity over 24 hours.

